AQA A-LEVEL: Biopsychology - Localisation of Function
LOCALISATION OF FUNCTION
LOCALISATION: Theory that specific areas of the brain are associated w/ particular physical and physiological functions.
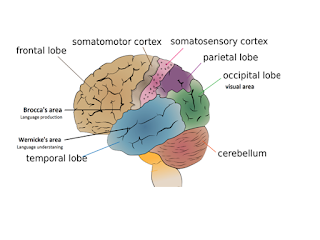
MOTOR CORTEX contains the Frontal Lobe
SOMATOSENSORY CORTEX contains the Parietal Lobe
VISUAL CORTEX contains the Occipital Lobe
AUDITORY CORTEX contains the Temporal Lobe
Language systems are in the
WERNICKE'S AREA for Speech Comprehension and BROCA'S AREA for Speech Production
LASHLEY's Research - Localisation is incorrect, his research supports the idea of equipotentiality of the cortex. Simple functions are localised but complex functions are not
LOCALISATION: Theory that specific areas of the brain are associated w/ particular physical and physiological functions.
MOTOR CORTEX contains the Frontal Lobe
SOMATOSENSORY CORTEX contains the Parietal Lobe
VISUAL CORTEX contains the Occipital Lobe
AUDITORY CORTEX contains the Temporal Lobe
Language systems are in the
WERNICKE'S AREA for Speech Comprehension and BROCA'S AREA for Speech Production
" My Father Sings Praise" "Violets Only Around Trees" "Women Can Bring Power"HEMISPHERIC LATERALISATION: Dominance of one are of the brain for a particular physical and physiological function
LASHLEY's Research - Localisation is incorrect, his research supports the idea of equipotentiality of the cortex. Simple functions are localised but complex functions are not
MOTOR CORTEX
- Generates voluntary motor movements by sending messages to muscles via CNS
- In the frontal lobe, both right and left hemispheres have motor cortex
- Contralateral - Right side controls left body, Left side controls right body
- Damage to one side of brain will affect the control of movement on opposite side of body
- Somatotopically organised - point for point correspondence of an area of the body to a point on the CNS
SOMATOSENSORY CORTEX
- Detects sensory events from different areas in the body, more so the skin such as touch, pressure, pain and temperature
- In the parietal lobe, both hemispheres have a somatosensory cortex
- Contralateral
- Right side receives sensory info from left side of body, Left side receives sensory info from right side of body
- Damage to one side of brain will affect the control of movement on opposite side of body
- Somatotopically organised - point for point correspondence of an area of the body to a point on the CNS
VISUAL CORTEX
- Largest system in the brain. Located in the occipital lobe. Visual processing starts in retina and info in the form of nerve impulses are transferred to the optic nerve.
- Visual cortex is in both hemispheres, is contralateral, takes in visual information such as colour, shape or movement
- HUROVITZ et al - Damage to visual cortex can lead to complete loss of all vision
AUDITORY CORTEX
- Concerned w/ hearing, is in the temporal lobe of both hemispheres of brain and is contralateral
- Auditory pathways start in the cochlea where info is sound waves then impulses which travel to the brainstem to the thalamus and auditory cortex
- Damage to auditory cortex results in issues processing sounds rather than deafness
BROCA'S AREA
- Language centre in the back frontal lobe, this area is for speech production
- PT's who had lesions in their left frontal lobe couldn't speak or write
WERNICKE'S AREA
- In the back area of the left temporal lobe and is for speech comprehension, pts with lesions in this area could speak but not comprehend language
Both language centres work together to process and produce language.
HEMISPHERIC LATERALISATION
LEFT SIDE - VALL (Language)
- Verbal aspects of consciousness
- Analytical reasoning
- Logic
- Linguistic Skills
RIGHT HEMISPHERE - SHAME (Spatial)
- Spatial
- Holistic
- Artistic
- Musical
- Emotional
HELLER AND LEVY 1981- Right side of brain dominant for Facial recognition of emotions. If there was a split photo of someone half smiling half neutral pt's would recognise the left side (picture on left goes through right side of brain)
EVALUATION
RESEARCH SUPPORT from human clinical case studies
- There was receptive aphasia following damage to the Wernicke's area and amnesia following damage to specific areas of the hippocampus.
Much of the Language Centre research comes from CASE STUDIES
- These studies involve individuals and because it's post mortem research you can only pinpoint some areas but not get the individual to do further tasks, modern methods are more accurate.
Spemy's research uses a MIX of Quasi-experiments and Clinical Studies
- So he was able to combine quantitative and qualitative data, and the use of combining methods means there was a wide variety of statistically reliable data info
ALTERNATIVE THEORY by Lashley which is MORE HOLISTIC
- Lashley's experiment on rats supports equipotentiality of the cortex and suggests only a few brain functions are localised such as simple and vital functions like motor control but complex functions are not localised

Really I appreciated the effort you made to share the knowledge. Thank you!
ReplyDeletehttps://blog.mindvalley.com/motor-cortex/