AQA A-LEVEL: Biopsychology - Nervous System
DIVISIONS of NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Both sub-branches are usually in balance but under relaxed/stressed circumstances the balance shifts and one become more dominant in the "Flight or Fight" response. Sub-branches keep the body in a state of homoeostasis, many of its functions are automatic, require little conscious thought.
Both sub-branches are usually in balance but under relaxed/stressed circumstances the balance shifts and one become more dominant in the "Flight or Fight" response. Sub-branches keep the body in a state of homoeostasis, many of its functions are automatic, require little conscious thought.

THE CNS
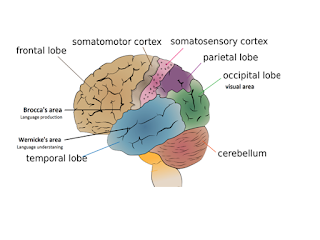
The Brain
- Monitors and regulates primitive bodily processes such as breathing, digestion, heartbeat
- Involved in higher order thinking such as planning and problem-solving w/ the pre-frontal cortex
The Spine
- Relays info between the brain and body using neurones
- Connects from spinal nerves (which govern reflex actions) to muscles, effectors and glands
- Co-ordinates bodily movement, damage to this area affects mobility and speech
THE PNS
Somatic Nervous System
- Involved w/ involuntary movement of skeletal muscles, orchestrates via brain
- Has 12 Cranial nerves (on underside of brain) and 31 Spinal nerves
- Has both sensory and motor neurones
- Transmits and receives sensory info
Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic Branch
- When exposed to a stress, the sympathetic branch is activated, prepares body for rapid action
- Increases heart rate and breathing to increase blood flow and oxygen, dilates pupils for better awareness, perspiration to regulate body temperature
- Slows down non-essential activities which consume energy like digestion
Parasympathetic Branch
- Involved when the threat has passed when body is trying to store and conserve energy
- Returns body to a state of relaxation slows down breathing + heart rate and increases digestion

Comments
Post a Comment